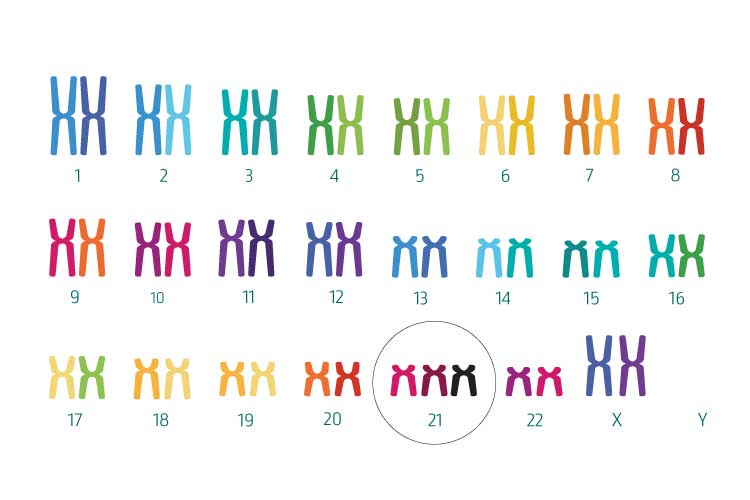
Trisomy 21 (Down Syndrome)
Trisomy 21 is caused by an extra copy of chromosome 21 and isthe most common form of chromosomal disorder in humans. This trisomy leads to Down syndrome, which is associated with usually moderate intellectual disability and other disorders, such as congenital heart disease. Trisomy 21 occurs in 1 in 500 pregnancies. About a third of pregnancies with trisomy 21 end in miscarriage. Therefore, it is estimated that only 1 in 830 newborns has trisomy 21. The likelihood of trisomy 21 is largely related to the mother's age. For example, the risk of trisomy 21 in a 20-year-old pregnant woman is on average 1 in 1,050, while the risk in a 40-year-old pregnant woman is about 1 in 100 (information from the end of the first trimester).